[course05] 02 Two-dimen
Declare and initialize
int[][] A;
A = new int[3][4];
int[][] A = { { 1, 0, 12, -1 },
{ 7, -3, 2, 5 },
{ -5, -2, 2, -9 }
};
A = new int[][] { { 1, 0, 12, -1 },
{ 7, -3, 2, 5 },
{ -5, -2, 2, -9 }
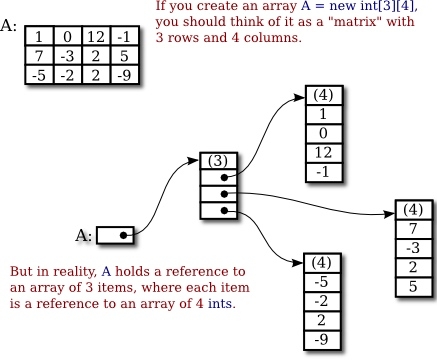
};The truth about 2D arrays
Last updated