[course05] 03 ArrayList
ArrayList and Parameterized Types
ArrayList<String> namelist;
namelist = new ArrayList<String>();
ArrayList<Player> playerList = new ArrayList<Player>();
//in java 10 or later
var playlerList = new ArrayList<Player>();method
Programming with ArrayList
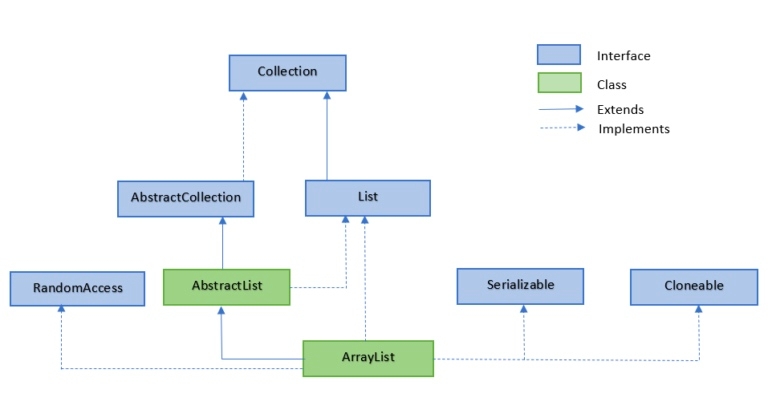
ArrayList interface
Last updated