[homework-java] course04
[homework-java] course04
作业说明
下载 CollapsarHomeworkWeek3 文件。拷贝到week3的包中。
打开CollapsarHomeworkWeek3.java 文件, 运行一下。
在Edit Configuration中设置对应的参数,在VM options内添加-ea参数
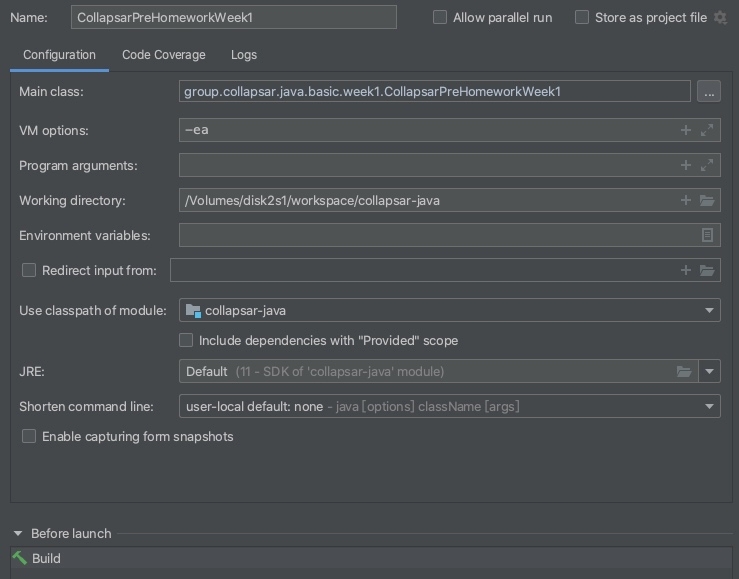
后面执行的时候如果看到Passed 说明用例通过,如果看到异常说明当前用例有问题,需要修改。

作业内容
1. encodeRightLeftRouteCipher(message,rows)
Background: A right-left route cipher is a fairly simple way to encrypt a message. It takes two values, some plaintext and a number of rows, and it first constructs a grid with that number of rows and the minimum number of columns required, writing the message in successive columns. For example, if the message is WEATTACKATDAWN, with 4 rows, the grid would be:
We will assume the message only contains uppercase letters. We'll fill in the missing grid entries with lowercase letters starting from z and going in reverse (wrapping around if necessary), so we have:
Next, we encrypt the text by reading alternating rows first to the right ("WTAW"), then to the left ("NTAE"), then back to the right ("ACDz"), and back to the left ("yAKT"), until we finish all rows. We precede these values with the number of rows itself in the string. So the encrypted value for the message WEATTACKATDAWN with 4 rows is "4WTAWNTAEACDzyAKT".
With this in mind, write the function encodeRightLeftRouteCipher that takes an all-uppercase message and a positive integer number of rows, and returns the encoding as just described.
Here are a few more examples to consider:
Be sure to take the time to fully understand each of those examples!
Hint: the grid described above is only conceptual. Your code will never actually construct a 2-dimensional grid (especially as you may not yet use lists!). Instead, you should use a clever scheme of indexing the message string where you translate a row and column into a single index into the message string.
More complete hint: let's do this example in a bit more detail, and we'll even provide an idea or two on how to simplify solving this:
Find the dimensions of the conceptual 2d grid Since len('WEATTACKATDAWN') is 14, and we have 3 rows, we need math.ceil(14/3) or 5 columns.
Pad the string We need 3*5, or 15 letters. We have 14. We have to add one. So we now have 'WEATTACKATDAWNz'
Imagine the conceptual 2d grid We do not create this part. We just imagine it. But this is the 2d grid we imagine:
4. Label your rows and cols To be sure we are visualizing the grid properly, let's add row and col labels, like so:
Label the padded string with row, col, and i Let's use these row and col labels, but write them over the padded string (instead of the conceptual 2d grid). We'll also include the index i, like so:
Find a function f(row,col) --> i Look at the patterns in the row, col, and i in the table we just made. See if you can find a function f(row, col) that takes any row and col (in the conceptual 2d grid) and returns the corresponding index i (in the padded string). Also, name this function something better than f.
Hint: from the table above, we see that the K is in row 1 and column 2, and the K is at index 7 in the padded string, so...
f(1,2) == 7Hint: see how the row in the table above repeats: 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2,... What does this have to do with the fact that we have 3 total rows?
Now, traverse the 2d grid top-to-bottom, left-to-right This step is not required, but it is super helpful. As only a temporary measure, we will solve a slightly easier version of the problem: we will simply ignore that every other row goes right-to-left. We'll make every row go left-to-right just for now. So use two loops, one going over every row, and inside that, one going over every column. For each row,col pair, use your function f() that you just wrote (and renamed) to find the index in the padded string. Remember that this was the conceptual grid:
Now alternate left-to-right and right-to-left Now make every-other-row go the other way. So the second row will change from ETKDN to NDKTE, like so:
Add the rows as a prefix Easy enough:
Return that string We are done. To remind ourselves, here was the test case:
3.decodeRightLeftRouteCipher(message)
Write the function decodeRightLeftRouteCipher, which takes an encoding from the previous problem and runs it in reverse, returning the plaintext that generated the encoding. For example, decodeRightLeftRouteCipher("4WTAWNTAEACDzyAKT") returns "WEATTACKATDAWN".
Last updated