[course03] 03 for loops
For Loops
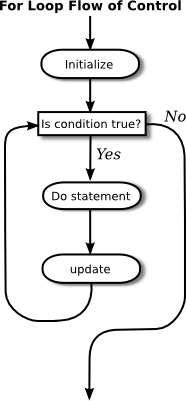
initialization
while ( continuation-condition ) {
statements
update
}years = 0; // initialize the variable years
while ( years < 5 ) { // condition for continuing loop
interest = principal * rate; //
principal += interest; // do three statements
System.out.println(principal); //
years++; // update the value of the variable, years
}
// the same as
for ( years = 0; years < 5; years++ ) {
interest = principal * rate;
principal += interest;
System.out.println(principal);
}
examples: how many different letters were found
example : Demonstrates "for" loop by listing
ForEach syntax
Scope
Last updated