[homework]course03 作业
[homework]course03 作业
Python 3.9 及以下:
下载 collapsar_week2_linter.py和 collapsar_hw_week2.py文件。拷贝到week2的文件夹中。
其中collapsar_week2_linter.py文件不需要改动
Python 3.10 及以上:
打开collapsar_hw_week2.py 文件
作业
1. integral(f, a, b, N) [可选做]
Background: in calculus, we use the integral of a function f from x=a to x=b to compute the area under the curve between those points (or the negative area if the function is below the x-axis). One way to approximate this area (that is, to find it without doing any actual calculus!) is by replacing the smooth function with a collection of N trapezoids, as shown in this image (from here, with N=5): 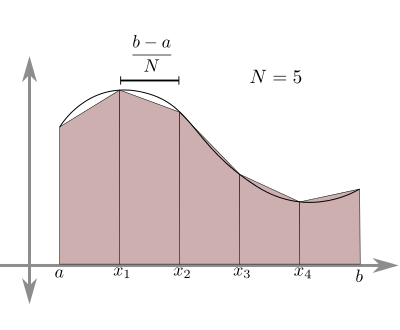
As in that image, here we will only use uniform widths, so each of the trapezoids has a width of (b - a)/N, so that all N of them together span the width of (b - a).
In any case, the larger N is, the more trapezoids you use, the more accurate your approximation becomes. You can read more here about this so-called trapezoidal rule.
With this in mind, write the function integral(f, a, b, N) that takes a Python function f (that itself takes one value x, a float, and returns a float), and two floats a and b, where a
Hint: you should use almostEqual if you have your own tests or add any to our test function. Also, you'll probably want to use some very simple curves for testing, as we did in the test function, such as f(x)=x, f(x)=2x+3, and f(x)=2x**2, and then in ranges (a,b) with values of N such that you can fairly easily compute the expected answer by hand.
Another hint: here is a basic example showing how functions work as parameters to other functions:
def f1(x): return x+1 def f2(x): return x+2 def h(f): return f(10) print(h(f1)) # calls f1(10), prints 11 print(h(f2)) # calls f2(10), prints 12
2. nthSmithNumber(n)
Write the function nthSmithNumber that takes a non-negative int n and returns the nth Smith number, where a Smith number is a composite (non-prime) the sum of whose digits are the sum of the digits of its prime factors (excluding 1). Note that if a prime number divides the Smith number multiple times, its digit sum is counted that many times. For example, 4 equals 2**2, so the prime factor 2 is counted twice, thus making 4 a Smith Number.
**3. playPig() **
First, read about the dice game Pig here. Then, write the function playPig(), that allows two players to play the game Pig. You will want to use random.randint(1,6) to randomly choose a number between 1 and 6 inclusive. Grading criteria:
Your game must enforce the basic rules of Pig.
Your game should not use any graphics. This is a console-based game.
Your game should use the input(prompt) function to get user input.
Your game should print enough information to make the game reasonably fun and usable.
As with the previous creative problem, be thoughtful but don't overthink this. Any reasonably fun, playable game of Pig will do fine here. Have fun!
4. Code Writing: nthHappyPrime
Write the function nthHappyPrime(n) that finds the nth happy prime. Prime we know already, but what is a happy number? To find out, read the first paragraph on the Wikipedia page. For our purposes, we can simplify the process of finding a happy number by saying that a cycle which reaches 1 indicates a happy number, while a cycle which reaches 4 indicates a number that is unhappy. To solve this problem, you'll want to use isPrime and write three other functions:
sumOfSquaresOfDigits
Write the function sumOfSquaresOfDigits(n) which takes a non-negative integer and returns the sum of the squares of its digits. For example, 123 would become 1^2 + 2^2 + 3^2 = 1 + 4 + 9 = 14. You must work with the number input directly instead of casting it to a string! Even if the linter allows your code, we will also check for this requirement in AutoLab!
isHappyNumber
Write the function isHappyNumber(n) which takes a possibly-negative integer and returns True if it is happy and False otherwise. Note that all numbers less than 1 are not happy.
nthHappyPrime
A happy prime is a number that is both happy and prime. Write the function nthHappyPrime(n) which takes a non-negative integer and returns the nth happy prime number (where the 0th happy prime number is 7).
5. Code Writing: printNumberTriangle(n)
Instead of returning a value, in this function you'll be printing out results. Write the function printNumberTriangle that takes one non-negative integer, n, and prints out a number triangle based on n. For example, given the number 4, this function would print out
Last updated