[course01] 辅助阅读 How does JRE and jdk works
[course01] 辅助阅读 How does JRE and jdk works
What does JRE consists of?
JRE consists of the following components:
Deployment technologies, including deployment, Java Web Start and Java Plug-in.
User interface toolkits, including Abstract Window Toolkit (AWT), Swing, Java 2D, Accessibility, Image I/O, Print Service, Sound, drag and drop (DnD) and input methods.
Integration libraries, including Interface Definition Language (IDL), Java Database Connectivity (JDBC), Java Naming and Directory Interface (JNDI), Remote Method Invocation (RMI), Remote Method Invocation Over Internet Inter-Orb Protocol (RMI-IIOP) and scripting.
Other base libraries, including international support, input/output (I/O), extension mechanism, Beans, Java Management Extensions (JMX), Java Native Interface (JNI), Math, Networking, Override Mechanism, Security, Serialization and Java for XML Processing (XML JAXP).
Lang and util base libraries, including lang and util, management, versioning, zip, instrument, reflection, Collections, Concurrency Utilities, Java Archive (JAR), Logging, Preferences API, Ref Objects and Regular Expressions.
Java Virtual Machine (JVM), including Java HotSpot Client and Server Virtual Machines.
How does JRE works?
To understand how the JRE works let us consider a Java source file saved as Example.java. The file is compiled into a set of Byte Code that is stored in a “.class” file. Here it will be “Example.class“.
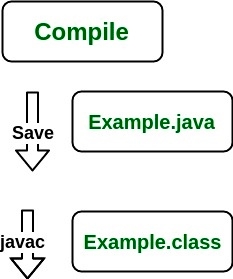
The following diagram depicts what is done at compile time.
The following actions occur at runtime.
Class Loader:The Class Loader loads all necessary classes needed for the execution of a program. It provides security by separating the namespaces of the local file system from that imported through the network. These files are loaded either from a hard disk, a network or from other sources.
Byte Code Verifier:The JVM puts the code through the Byte Code Verifier that checks the format and checks for an illegal code. Illegal code, for example, is code that violates access rights on objects or violates the implementation of pointers.
The Byte Code verifier ensures that the code adheres to the JVM specification and does not violate system integrity.
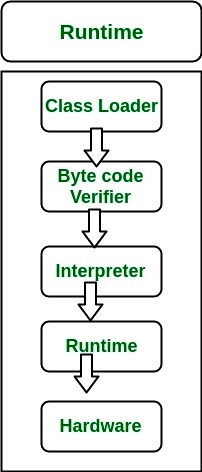
Intrepreter: At runtime the Byte Code is loaded, checked and run by the interpreter. The interpreter has the following two functions:
Execute the Byte Code
Make appropriate calls to the underlying hardware
Both operations can be shown as:
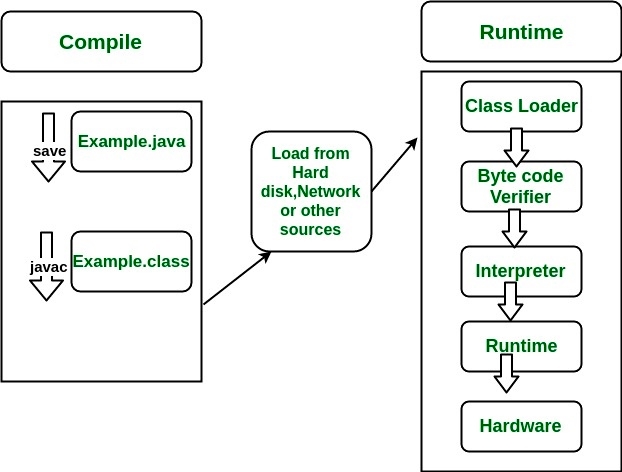
To understand the interactions between JDK and JRE consider the following diagram.
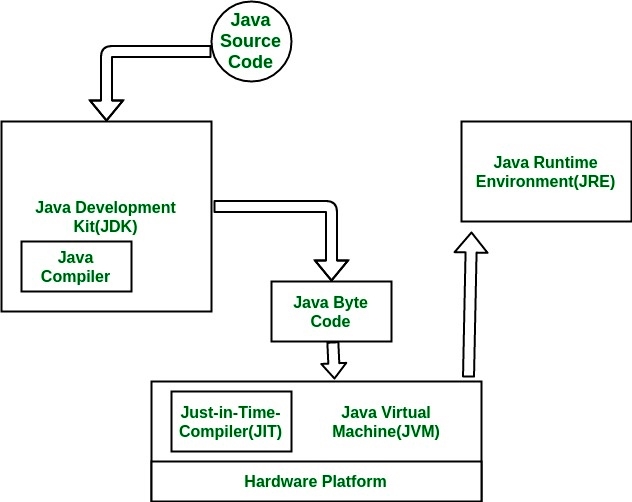
How does JVM works?
JVM becomes an instance of JRE at runtime of a Java program. It is widely known as a runtime interpreter.JVM largely helps in the abstraction of inner implementation from the programmers who make use of libraries for their programmes from JDK. For detailed working of JVM click ->Working of JVM
Last updated