[course05] homework
[course05] homework
Q1 Game
This question involves simulation of the play and scoring of a single-player video game. In the game, a player attempts to complete three levels. A level in the game is represented by the Level class.
public class Level {
/** Returns true if the player reached the goal on this level and returns false otherwise */
public boolean goalReached() {
/* implementation not shown */
}
/** Returns the number of points (a positive integer) recorded for this level */
public int getPoints() {
/* implementation not shown */
}
// There may be instance variables, constructors, and methods that are not shown.
}Play of the game is represented by the Game class. You will write two methods of the Game class.
(a) Write the getScore method, which returns the score for the most recently played game. Each game consists of three levels. The score for the game is computed using the following helper methods.
The isBonus method of the Game class returns true if this is a bonus game and returns false otherwise.
The goalReached method of the Level class returns true if the goal has been reached on a particular level and returns false otherwise.
The getPoints method of the Level class returns the number of points recorded on a particular level. Whether or not recorded points are earned (included in the game score) depends on the rules of the game, which follow.
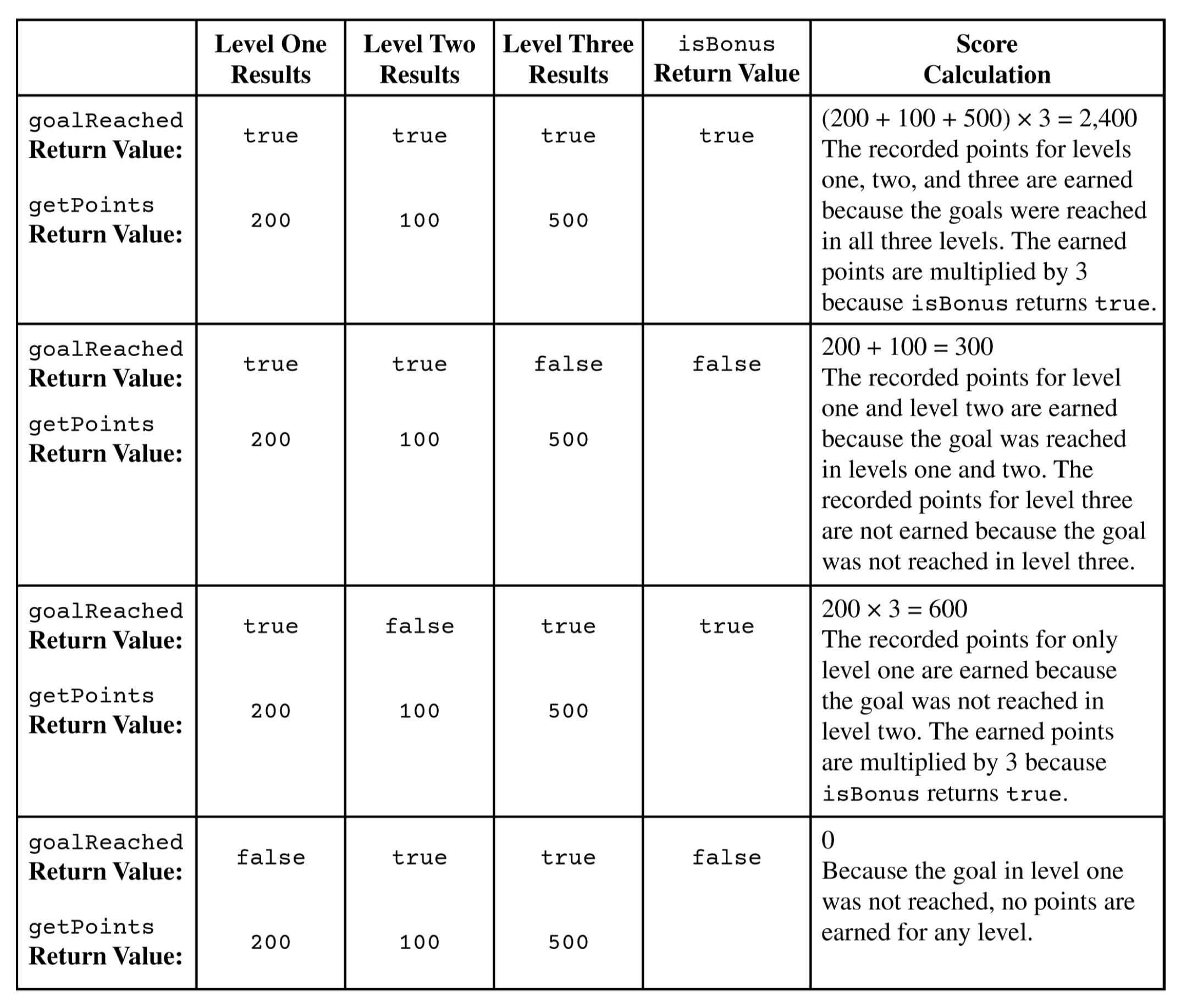
The score for the game is computed according to the following rules.
Level one points are earned only if the level one goal is reached. Level two points are earned only if both the level one and level two goals are reached. Level three points are earned only if the goals of all three levels are reached.
The score for the game is the sum of the points earned for levels one, two, and three.
If the game is a bonus game, the score for the game is tripled.
The following table shows some examples of game score calculations.
Complete the getScore method.
(b) Write the playManyTimes method, which simulates the play of num games and returns the highest game score earned. For example, if the four plays of the game that are simulated as a result of the method call playManyTimes(4) earn scores of 75, 50, 90, and 20, then the method should return 90.
Play of the game is simulated by calling the helper method play. Note that if play is called only one time followed by multiple consecutive calls to getScore, each call to getScore will return the score earned in the single simulated play of the game.
Complete the playManyTimes method. Assume that getScore works as intended, regardless of what you wrote in part (a). You must call play and getScore appropriately in order to receive full credit.

Q2 Log Message
This question involves two classes that are used to process log messages. A list of sample log messages is given below.
Log messages have the format machineId:description, where machineId identifies the computer and description describes the event being logged. Exactly one colon (":") appears in a log message. There are no blanks either immediately before or immediately after the colon.
The following LogMessage class is used to represent a log message.
(a) Write the constructor for the LogMessage class. It must initialize the private data of the object so that getMachineId returns the machineId part of the message and getDescription returns the description part of the message.
Complete the LogMessage constructor below.
(b) Write the LogMessage method containsWord, which returns true if the description in the log message properly contains a given keyword and returns false otherwise.
A description properly contains a keyword if all three of the following conditions are true.
the keyword is a substring of the description;
the keyword is either at the beginning of the description or it is immediately preceded by a space;
the keyword is either at the end of the description or it is immediately followed by a space.
The following tables show several examples. The descriptions in the left table properly contain the keyword "disk". The descriptions in the right table do not properly contain the keyword "disk".

Assume that the LogMessage constructor works as specified, regardless of what you wrote in part (a). Complete method containsWord below.
Last updated