IGCSE cs 0478 2023 spec 2b 13
IGCSE cs 0478 2023 spec 2b 13
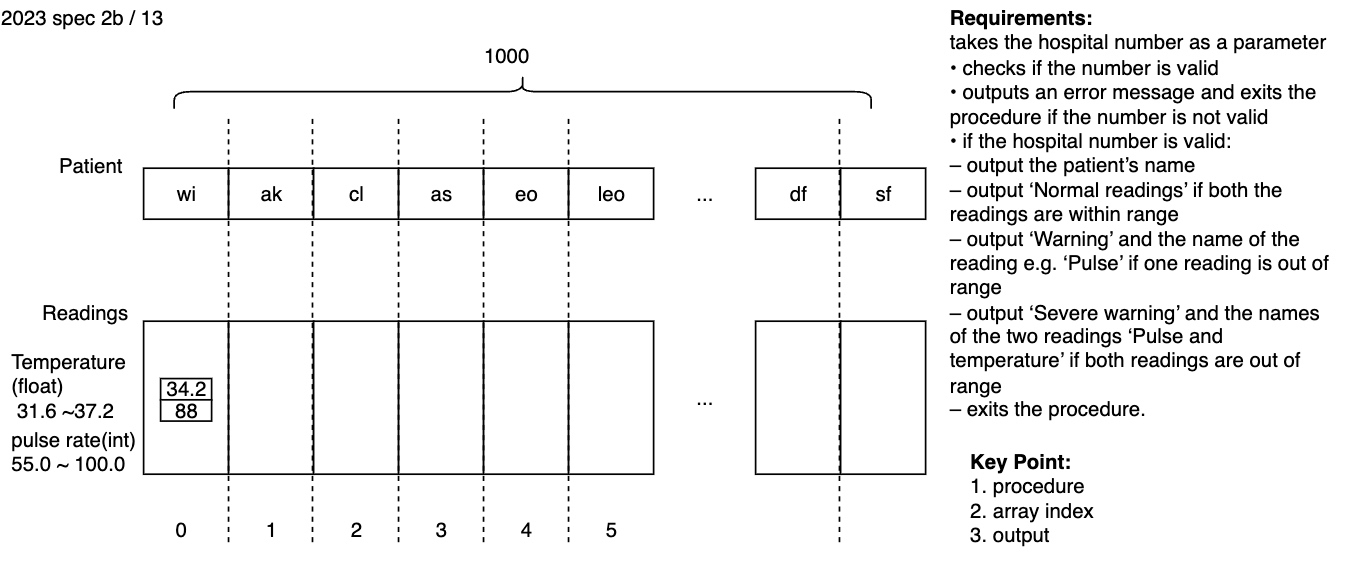
The names of patients are stored in the one-dimensional (1D) array Patient[] of type string. A separate two-dimensional (2D) array Readings[] stores the latest data recorded about each patient. The array already contains the readings taken by a nurse for each patient:
• temperature measured to one decimal place • pulse rate, a whole number.
Temperature readings should be in the range 31.6 to 37.2 inclusive.
Pulse readings should be in the range 55.0 to 100.0 inclusive.
The hospital number given to the patient is used for the index on both arrays, this is a value between 1 and 1000 inclusive.
When the data for a patient is checked a warning is given if any of the readings are out of range. If both readings are out of range, then a severe warning is given.
Write a procedure, using pseudocode or program code, that meets the following requirements:
takes the hospital number as a parameter
checks if the number is valid
outputs an error message and exits the procedure if the number is not valid
if the hospital number is valid:
output the patient’s name
output ‘Normal readings’ if both the readings are within range
output ‘Warning’ and the name of the reading e.g. ‘Pulse’ if one reading is out of range
output ‘Severe warning’ and the names of the two readings ‘Pulse and temperature’ if both readings are out of range
exits the procedure.
You must use pseudocode or program code and add comments to explain how your code works.
You do not need to initialise the data in the arrays.
Python版初始化代码,练习的时候使用如下的代码
图解
Python版答案
Last updated